Monday, June 29, 2009
Understanding Bash (Part 2)
Selected Options for Bash Prompt:
\h (Hostname)
\u (Username of the current user)
\w (current working directory, with the top-level directory as ~)
\W (base name of the current working directory, with top-level directory as ~)
How do we get BASH to look like below under CentOS
[root@test ~/scratch/tmp]$
# vim .bashrc
# export PS1='\e[1;33m[\u@\h \w]\$ \e[m'
\e[a;bm \e[m
(marks the start of the character the colour apply to.)
(a;bm is the color code)
(a can have a value of both 0 and 1. 1 will be the lighter colour of the 0)
For Color Codes, see Changing Colour for ls on BASH Blog
Special Feature Writeup of ISC09
HPCwire's special section dedicated to ISC09
Grand unification of supercomputing and cloud computing?
A good article where experts provide differing view on the feasibility of Cloud Computing on HPC infrastructure.
Saturday, June 27, 2009
Understanding Bash (Part 1)
- .bash_history (list of previously entered commands)
- .bash_logout (run a script when Bash exit)
- .bashrc (basic settings for prompt actions)
- .bash_profile (additional configuration. If .bash_profile is not present, the user account will use /etc/profile)
Adding a Directory to a Path
To add a directory to a path, edit the .bash_profile
$ vim .bash_profile
------------------------------
PATH=$PATH:/usr/local/bin
export PATH
------------------------------
Putting Aliases
One of the appropriate place to put aliases is in .bashrc
Friday, June 26, 2009
Using mrxvt
For more information,
- mrxvt project site
- Juggling Shells (by Linux Magazine)
Thursday, June 25, 2009
Changing Color for ls on Bash
Have you noticed that on a tty console, the colour of the directory is dark blue. It is so hard to read the blue text. How do we change the colours?
Step 1: Pipe the information from Dircolors and save as .dircolors
$ dircolors -p > ~/.dircolors
Step 2: Change the contents of .dircolors
$ vim .dircolors
#------------------------------------------------
NORMAL 00 # global default, although everything should be something.
FILE 00 # normal file
DIR 01;34 # directory
.........
#------------------------------------------------
Color Codes (Foreground):
00;30=Black
00;31=Red
00;32=Green
00;33=Brown
00;34=Blue
00;35 Magenta
00;36=Cyan
00;37=White
01;30=Grey
01;31=Light Red
01;32=Light green
01;33=Yellow
01;34=Light Blue
01;35=Pink
01;36=Light Cyan
01;37=Light Gray
Introduce DirColors to the new configuration
$ dircolors -b ~/.dircolors
Horray done.
Articles:
Monday, June 22, 2009
Using wget to download entire website
Remember that downloading entire website that is not yours is unethical and illegal as well.
# wget \
--recursive \
--no-clobber \
--page-requisites \
--html-extension \
--convert-links \
--restrict-file-names=windows \
--domains website.org \
--no-parent \
www.mywebsite.org/
The options are:
--recursive: download the entire Web site.
--domains website.org: don't follow links outside website.org.
--no-parent: don't follow links outside the directory tutorials/html/.
--page-requisites: get all the elements that compose the page (images, CSS and so on).
--html-extension: save files with the .html extension.
--convert-links: convert links so that they work locally, off-line.
--restrict-file-names=windows: modify filenames so that they will work in Windows as well.
--no-clobber: don't overwrite any existing files (used in case the download is interrupted and
resumed).
Sunday, June 21, 2009
Using Text-Mode Web Browser
- elinks
- links
- lynx
# yum install elinks links lynx
If you are using Debian Derivatives such as Linux Mint
# apt-get install elinks links lynx
To surf
$ elinks http://linuxtoolkit.blogspot.com
$ links http://linuxtoolkit.blogspot.com
$ lynx http://linuxtoolkit.blogspot.com
The one I used the most is lynx.
Saturday, June 20, 2009
Understanding Cat commands
1. To join files and display them on the screen
# cat file1 file2
2. To join 2 files together and save them on file 3
# cat file1 file2 > file3
3. To display the file with line numbering
# cat -n file1
Using yum effectively (Part 2)
There is one utility seldom used which is part of yum ie yumdownloader. Yumdownloader is a cool utility to download the rpm package instead of installing directly
Using yumdownloader# yum install yum-utils (download the yum-utils package)
# yumdownloader
# yumdownloader alpine (For example)
# yumdownloader --source (package-name)
Using the GUI yum installer
# yum install pirut
# pirut
Using yum effectively (Part 1)
Some important usages:
1. To install package
# yum install (
# yum -y install
2. To update package
# yum update
Launch the GUI for yum update
# yum install pirut
# pup
3. To use yum to install instead of rpm.
(Yum will search for dependencies and repositories)
# yum localinstall
4. Uninstalling Package
# yum remove
5. Listing Package
# yum list (
6. Group Install
# yum groupinstall (group-package-name)
Sunday, June 14, 2009
Distro of Choice for Desktop and Server
I have tested OpenSuse 10.3, Fedora 9, Ubuntu, I finally settled on Linux Mint. Its elegance and layout really "wow" me after I have installed and never look back. Besides, it has a whole load of software from Debian/Ubuntu Repository. I like the compilation of codecs which I can install with a click on the icon "Install Multimedia Codecs"
As for the Server OS of choice, I think CentOS is still my choice. No special reasons except that I just got used to Redhat Distro since I started using Redhat 6 on our servers.
Installing Dropbox on Linux Mint 6 (Ubuntu 8.10)
Step 1: Add the Dropbox repository to the Linux Mint package source file. The most suitable place in my opinion will be the application specific setup list ie /etc/apt/source.list.d/dropbox.list
# cd /etc/apt/source.list.d/
# touch dropbox.list
# vim dropbox.list
Go to http://www.getdropbox.com/download and cut and paste the repository information for Ubuntu 8.10 into /etc/apt/source.list.d/dropbox.list
deb http://linux.getdropbox.com/ubuntu intrepid mainStep 2: Update the Repository
deb-src http://linux.getdropbox.com/ubuntu intrepid main
# apt-get update
Step 3: Install Dropbox
# apt-get install nautilus-dropbox
Step 4: Restart Nautilus to start Dropbox
Step 5: Menu > Applications > Dropbox
The rest is as straight-forward as you can get.
Friday, June 12, 2009
Using vim more effectively
1. Searching
Create a .vimrc in your own home directory. With this you can you place useful commands settings
set incsearch (incremental search function) set ignorecase (ignore case-sensitive function) set smartcase (used in conjunction with ignorecase. By default it search for any case unless the user specify uppercase character)
2. Movement from the keyboard.
h (move left) l (move right) j (move up) k (move down)
3. Editing
x (delete the character under the cursor) y (copy the characters from the current cursor) p (paste previous deleted or copied text after the current cursor position) d (delete the characters from the cursor position)
4. File Browser and Screen
e .(To make vim act as a file browser) :split (To split the screen into seperate segments. Use Crtl+W and arrow keys to change screen)
5. UsingTab
# vim -p file1 file2 (2 file with tabs will show)
:tabn (next tab) :tabp (previous tab)
6. Spell Check
: setlocal spell spelllang=en_us (enable spell checking) : help spell (spell help) ]s (Go to the next misspelled word) z= (Display suggestions for correct spelling)
Interesting Articles:
Vim Introduction and Tutorial
Tuesday, June 9, 2009
Monday, June 8, 2009
rpm.livna.org Repository
In 2008 rpm.livna.org merged with two other package repositories into RPM Fusion. All packages have been moved there except one that RPM Fusion for various reasons didn't want to take.
# wget http://rpm.livna.org/livna-release.rpm
# rpm -Uvh livna-release.rpm
RPM Fusion Repository
Step 1:
You need to enable EPEL on RHEL5 or compatible distributions like CentOS before you enable RPM Fusion for EL.
Step 2: Download and install rpm package for CentOS
# wget
RPM Fusion free for RHEL5 or compatible like CentOS
RPM Fusion nonfree for RHEL5 or compatible like CentOS
For more information for Fedora and the above information, go to RPM Fusion Configuration
Friday, June 5, 2009
Understanding Login Sequence
When a user login, the environment variables are set following the below order
- /etc/profile (for all users)
- /etc/profile.d (Application specific setup)
- ~/.bash_profile
- ~/.bashrc
For further information, read Login Sequence
Wednesday, June 3, 2009
Changing the hostname on CentOS
# vim /etc/sysconfig/networkChange
HOSTNAME=myserver.name.com
Step 2: Edit /etc/hostname
# vim /etc/hostnameChange
myserver.name.com
Step 3: Run hostname
# hostname -F /etc/hostname
Monday, June 1, 2009
Setting hardware Clock to System Time
# hwclock --systohc
Setting up NTP Server for Local Network
The Network Time Protocol (NTP) is a protocol for synchronizing the clocks of computer systems over packet-switched, variable-latency data networks. NTP uses UDP on port 123 as its transport layer.
Setting Up NTP Server
Step 1: Install NTP Server and Client
# yum install ntp
Step 2: Configuration at /etc/ntp.conf
(The Basic Configuration is sufficient. A few things to note)
# vim /etc/ntp.conf
(Inside the /etc/ntp.conf) This statement is to allow local network to access the Server...
restrict 192.168.1.0 mask 255.255.255.0 nomodify notrap
(Inside the /etc/ntp.conf) Ensure the localhost has full access without any restructing password
restrict 127.0.0.1
Step 3: Start the Services
# chkconfig --levels 235 ntpd on
# ntpdate 0.pool.ntp.org
# service ntpd start
Check whether it is working
# ntpq -p
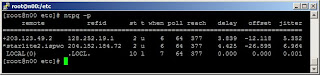
Setting Up NTP Clients to sync with the local NTP Server and NTP Client
Step 1: Install the ntpd services
# yum install ntp
Step 2: Configure the /etc/ntp.conf
# vim /etc/ntp.conf
(Inside the /etc/ntp.conf) Point to the local NTP Server
server 192.168.1.1
Step 3: Start the Services
# chkconfig --levels 235 ntpd on
# ntpdate 192.168.1.1
# service ntpd start
Check whether it is working
# ntpq -p
For more readings:
- How to Setup a Time Server in Linux from TechGuruLive (Debian-Based Server)

